Please Choose Your Language
+86-512-52396378
sales@szuniking.com
sales@szuniking.com
1 Longteng Rd, Tonggang Industrial Park, Changshu ETDZ, Jiangsu Province, China 215511
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-09-08 Origin: Site







You see polyamide in many things around you. This material is a polymer with repeating units. These units are joined by amide bonds. You can spot these bonds by the CO-NH group in its structure. Polyamide is important in materials science. It is strong, flexible, and can handle heat. Every year, industries make about 12 million tons of polyamide. The automotive sector uses the most polyamide. They use it because it lasts long and resists heat.
In 2024, people made 12 million tons of polyamide worldwide.
Polyamide 6 was more than half of the market, worth $42.6 billion.
The automotive industry used almost 40% of all polyamide.
Polyamide is a tough and bendy material. It is made of repeating units joined by amide bonds. The way polyamide chains are arranged changes its properties. Straight chains make it hard. Messy chains make it bendy. Polyamide takes in water. This can change how strong or bendy it is. Fillers can help keep its properties the same. There are different kinds of polyamide, like nylon. Each kind has special features and uses. Polyamide is used in cars and medical tools. Polyamide fabric is strong and useful. It is great for clothes, sports gear, and many daily products.
Polyamide is like a chain with repeating units. Each unit connects to the next by an amide bond. This bond has a carbonyl group and a nitrogen atom. The -CO-NH- group forms the backbone of polyamide. Amide bonds help chains stick together with hydrogen bonds. The carbonyl oxygen pulls hydrogen from other chains. The NH group gives hydrogen to nearby chains. This network makes polyamide strong and stable.
How the chains are arranged changes the material’s properties. Sometimes, chains line up neatly. These are crystalline regions. They make polyamide stiff and strong. Other times, chains are messy and not lined up. These are amorphous regions. They help polyamide absorb impacts and bend without breaking.
Tip: How the chains are arranged decides if polyamide is stiff or flexible.
Here is a table showing how different arrangements change polyamide:
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Crystalline Regions | Neatly lined chains give more strength and stiffness. |
Amorphous Regions | Messy chains help absorb impacts and make polyamide tougher. |
Intermolecular Interactions | Hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces keep polyamide stable, even when it gets hot. |
Adding fillers can make polyamide better. Carbon nanotubes and long carbon fibers make it stronger and more stretchy. Fillers also help block water, so polyamide lasts longer.
Polyamide is special because it has many good properties. It is strong, flexible, and can handle heat. Amide bonds help the chains form strong hydrogen bonds. This makes polyamide tough and stable when it gets hot.
Here are some important properties of polyamide:
High strength: Polyamide can hold heavy things and does not break easily.
Good flexibility: You can bend or stretch it and it will not snap.
Excellent resistance to wear: Polyamide lasts a long time, even if you use it a lot.
Impressive resistance to heat: It keeps its shape and strength when it gets hot.
Notable resistance to chemicals: Some types, like Nylon 6,10 and Nylon 12, do not get damaged by chemicals.
Resistance to UV and weather: Some polyamides, like Nylon 11, do not get ruined by sunlight or rain.
Here is a table comparing different types of polyamide:
Polyamide Type | Melting Point | Tensile Strength | Chemical Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
Nylon 6,6 (PA 66) | High melting point | Good tensile strength | Poor chemical resistance |
Nylon 6 (PA 6) | Decent melting point | Moderate tensile strength | Moderate chemical resistance |
Nylon 6,10 (PA 610) | Moderate melting point | High tensile strength | Good chemical resistance |
Nylon 11 (PA 11) | High melting point | High tensile strength | Good chemical resistance |
Nylon 12 (PA 12) | Moderate melting point | Good tensile strength | Good chemical resistance |
Polyamide can soak up water from the air. This can change how it works. When polyamide takes in water, it gets less strong and stiff. But it also gets more flexible and tough. Fillers can help stop water from changing polyamide too much.
Polyamide gets heavier when it absorbs water.
Water changes how strong and stretchy polyamide is.
Polyamide gets softer when it absorbs water.
Fillers like carbon fibers help polyamide stay strong, even when it is wet.
Note: Polyamide absorbs water, which makes it different from other polymers. You should think about this when you pick polyamide for something that needs steady properties.
Polyamide is used in many industries because it is strong, flexible, and resists heat and chemicals. You can find it in cars, electronics, and medical devices. You can change its properties by changing its structure or adding fillers. This makes polyamide useful for many things.
Some people think polyamide and nylon are the same. They are not. Polyamide is a big group of polymers. Nylon is just one kind of synthetic polyamide. You can say nylon belongs to the polyamide family. Nylon has an aliphatic structure, so its chains do not form rings. Other polyamides, like PA11 and PA12, have different structures and properties.
You see nylon a lot in clothes, car parts, and things people use every day. Other polyamides are found in packaging, electronics, and medical devices. The way you make these materials is also different. Here is a table that shows how they are made and what that means for how you use them:
Manufacturing Method | Description | Implications for End-Use Applications |
|---|---|---|
Polycondensation | React diamines with dicarboxylic acids or diacid chlorides | Lets you create many polyamide types with special properties |
Ring-Opening Polymerization | Polymerize lactams like caprolactam (Nylon 6) | Used for making nylon with unique features |
Interfacial Polymerization | Form polyamide film at the interface of two immiscible solvents | Good for special uses needing unique properties |
Tip: Think about what you need before picking nylon or another polyamide. Nylon is good for clothes and car parts. Other polyamides might be better for electronics or medical tools.
Polyamide and nylon have a lot in common. Both are strong and tough. You can use them where you need things to last. They do not wear out or break easily. This makes them good for gears, bushings, and parts that rub together.
Here are some ways polyamide and nylon are alike:
Both have high tensile strength and last a long time.
You can use them in high-stress areas because they do not break easily.
Both resist chemicals, though the level depends on the type.
They both handle friction and harsh surfaces well.
Water resistance is a shared trait, but nylon absorbs more water. This helps in uses like fishing lines.
You can count on both polyamide and nylon for strong and tough materials. They work well in many industries, like cars and electronics.
Polyamide comes in many types. You can sort them by their structure and what they can do. Each type has special features for different jobs. The way polyamide is built changes how it works in real life.
Did you know? How the chains are made in polyamide decides if it bends, stays strong, or handles heat.
Here is a table that lists the main types of polyamide and what makes them special:
Type of Polyamide | Description |
|---|---|
Amorphous Polyamide | Does not have a set crystal shape, so it bends easily and is simple to make. |
Polyamide 6 (Nylon 6) | Used a lot because it is strong and stands up to chemicals. |
Polyamide 66 (Nylon 66) | Very strong and keeps its shape in heat, good for machines. |
Polyarylamide | Has ring shapes in its chains, which helps it handle heat and chemicals better. |
Polyphthalamide | Has some rings in its chains, so it is better with heat and chemicals than regular types. |
Polyaramid | Very strong and keeps its shape in heat, often used for safety gear. |
Polymer Blends | Mixes different polyamides to get the right features. |
Aliphatic polyamides have straight or branched chains. You find these in many things because they are strong and resist chemicals. They are used in clothes, car parts, and machine plastics. Aliphatic polyamide is good for gears, bearings, and parts that need to stop electricity. You also see them in sports gear and food packaging.
Here is a table that shows where aliphatic polyamide is used:
Industry | Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Automotive | Engine parts, Fuel systems, Electrical parts | Handles heat, Resists chemicals, Stops electricity |
Industrial | Bearings, Gears, Valves, Seals | Lasts long, Slides easily, Resists chemicals |
Consumer Goods | Sports gear, Home items | Tough, Bends well, Lasts long |
Electrical and Electronics | Connectors, Switches, Cases | Stops electricity, Handles heat, Resists chemicals |
Food Industry | Food packaging, Conveyor belts | Resists chemicals, Lasts long |
You will see that polyamide fabric from aliphatic polyamides is bendy and lasts a long time. These fabrics are used in clothes and for work.
Aromatic polyamides have ring shapes in their chains. These rings make them very strong and able to take a lot of heat. You find aromatic polyamide in safety clothes, electric parts, and space tools. The stiff chains and strong bonds make them tough and stable in heat.
Very strong
Stays stable in heat
Resists chemicals well
Does not dissolve in most liquids
Aromatic polyamide is great for hard jobs. You find polyamide fabric from aromatic polyamides in bullet-proof vests and factory filters. These fabrics can take heat and chemicals, so they are good for rough places.
Tip: Pick aromatic polyamide if you need something that can take a lot of heat and stress.

Polyamide fabric is used in lots of products. It is strong, flexible, and light. You can stretch it, and it goes back to its shape. It absorbs moisture, so you stay dry. The fibers do not wear out fast. Polyamide fabric can handle chemicals and heat. It also works well when it is cold.
Here is a table that shows what makes polyamide fabric special:
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Mechanical Resistance | Handles tension and loads without breaking. |
Elasticity and Flexibility | Moves with your body and keeps its shape. |
Lightness | Feels light and comfortable. |
Moisture Absorption | Absorbs water, so sweat does not build up. |
Durability | Resists wear and abrasion. |
Chemical Resistance | Stays strong with oils and chemicals. |
Thermal Resistance | Works well with mineral, animal, and vegetable oils. |
Low-Temperature Performance | Keeps strength in cold weather. |
Self-Lubricating Property | Reduces noise and friction. |
Processing Properties | You can cut and drill it for many uses. |
Polyamide fabric comes in different finishes. You can pick dull or shiny looks. Sometimes, the fibers pill or get dirty. You can choose the finish that works for you. Polyamide fabric is strong and stretchy. It does not stain or smell from oils. It handles moisture well, so you feel comfortable.
Suzhou UNIKING New Material Co., Ltd. makes high-quality polyamide fabric. They use advanced ways to make the fibers. Their HTPA and PA6 series are strong and last long. They use careful finishing to give you the best fabric.
Polyamide fabric is used in many industries. In cars, it is in seat covers, airbags, and panels. Electronics use it for insulation and flexible circuits. Hospitals use it for gowns, bandages, and filters.
Here are some common uses:
Car interiors and safety equipment
Electrical insulation and connectors
Medical textiles and filters
Sportswear and outdoor gear
Industrial conveyor belts and packaging
Polyamide fabric helps make strong and eco-friendly plastics. People now use bio-based polyamides to save oil. Reinforced polyamide fabric is even stronger and handles heat better. It is light and tough, so it can replace old materials.
Suzhou UNIKING New Material Co., Ltd. works on new ideas and research. Their polyamide fabric meets strict rules for quality. They help car, electronics, and medical companies with good products. You get great service and strong, eco-friendly fabric.
Tip: Pick polyamide fabric for tough jobs. It is strong, flexible, and works well every time.

Polyamide is made by a process called condensation. In this process, polyamide monomers join together. When two monomers connect, a small molecule like water leaves. This makes the chains longer. The –CO-NH– group forms the main part of polyamide. Condensing agents like triphenylphosphine and P2O5 help the reaction go faster and make stronger chains.
Polyamide monomers join and give off water or hydrogen chloride.
Special agents help the reaction make bigger molecules.
The process creates amide linkages, which make polyamide strong.
You must control the temperature and mixing very carefully. Suzhou UNIKING New Material Co., Ltd. uses special machines to make sure every batch is good. Their twin-screw extrusion lines mix the material well for even quality.
Tip: How you control the condensation process changes how polyamide turns out.
Amide bonds keep the polyamide chains together. These bonds form when the carboxyl group of one monomer reacts with the amine group of another. The reaction uses a nucleophilic acyl substitution mechanism. First, the carboxylate oxygen works with an agent to make an active ester. Then, the amine attacks, and the amide bond forms. This bond is very strong and does not break easily in water or heat.
Amide bonds make polyamide tough and last a long time. You find these bonds all along the polymer chain. They help polyamide resist wear and keep its shape in tough places.
Suzhou UNIKING New Material Co., Ltd. uses advanced tests to check polyamide quality. Their lab measures density, tensile strength, and surface roughness. You can see how different finishing methods change the surface of polyamide parts:
Method | Result | Surface Roughness (Ra) |
|---|---|---|
Precision Grinding | Better surface quality | 2.85 μm |
Magnetic Field-Assisted Finishing | Smoother surface | 0.89 μm |
BLAST Technology | Very smooth surface | 0.78 μm |
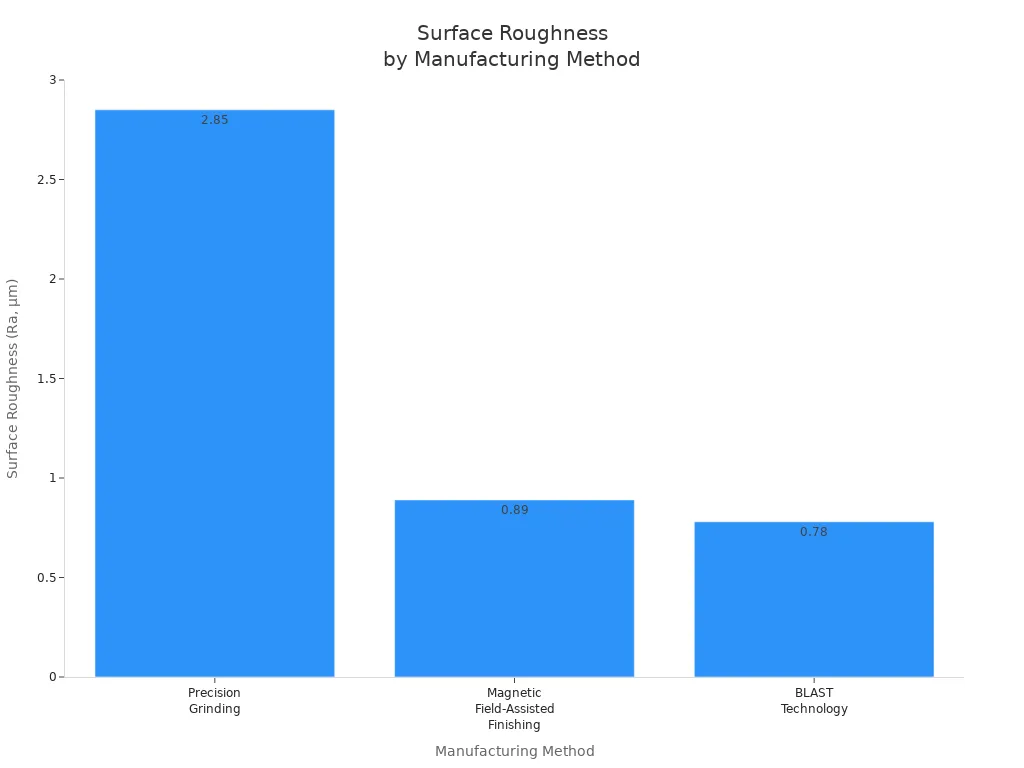
You get better results when you set printing parameters right and use post-process treatments. Testing mechanical properties helps you pick the best polyamide for your needs.
Polyamide is used in many ways. It is strong, flexible, and resists heat and chemicals. That is why you see it in lots of industries. Let’s see how polyamide is used in engineering plastics and things you use every day.
Polyamide is found in many engineering plastics. These plastics need to be tough and handle heat and chemicals. Polyamide works well for these jobs. Here is a table that shows where polyamide is used and why it is good:
Application Category | Specific Applications | Performance Advantages |
|---|---|---|
Powertrain Components | Air intake manifolds, Cylinder head covers, Engine covers, Oil pans, Transmission parts | High mechanical strength and stiffness, Excellent thermal resistance, Superior chemical resistance, Lightweight, Good wear and fatigue resistance |
Fuel and Cooling Systems | Fuel lines, Radiator end tanks, Thermostat housings | Maintains structural integrity under high temperatures, Contributes to vehicle weight reduction |
Electrical and Electronic Systems | Connectors, Wire harnesses, Sensor housings | Design flexibility, Allows for complex shapes and integrated functions |
Polyamide is strong, handles heat, and is light. In cars and electronics, this helps make things lighter and work better. Suzhou UNIKING New Material Co., Ltd. makes special polyamide products. Their products are high quality and used in cars, electronics, and factories.
Tip: Polyamide plastics help you make strong parts that last in tough places.
Polyamide is also used in many things you use every day. It is strong, bends easily, and does not wear out fast. Here are some common uses:
Printing ink and ballpoint pen ink
Ink binders, paints, and epoxy paints
Hot melt adhesives, seal coatings, varnishes, and lacquers
Rubber products, fishing lines, tents, gloves, and wheels
Strings for guitars and tennis rackets
Medical devices like implants and toothbrush bristles
Polyamide is great for clothes, sports gear, and things at home. It is strong and does not wear out quickly. In medicine, it is safe for the body and can be cleaned easily. Now, people use recyclable and bio-based polyamide films to help the environment.
Good factories use safe and careful ways to make polyamide. They follow rules like ISO 9001 and ISO 14001. Suzhou UNIKING New Material Co., Ltd. makes polyamide in a way that is safe for people and the planet. You can trust their polyamide for many uses.
You have learned that polyamide is strong and bends easily. It is made from repeating units joined by amide bonds. The table below shows the main ideas:
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Definition | Polyamides are tough, strong, and do not wear out fast. |
Chemical Structure | Made from repeating -CONH2 units. |
Main Types | Includes aliphatic, semi-aromatic, and aromatic types, like nylon-6 and Kevlar. |
Nylon is one kind of polyamide, but not all polyamides are nylon. Nylon is known for being flexible and easy to make into things. Other polyamides have their own special strengths. Polyamide fabric is important for eco-friendly and high-performance uses. You see it in sports clothes and car parts. Now you know how polyamide and nylon help make modern materials and support green solutions.
Polyamide is made of repeating units joined by amide bonds. These bonds have a carbonyl group (CO) and a nitrogen atom (NH). This setup makes polyamide strong and bendy.
Polyamide fabric is lighter and dries much faster than cotton. It stretches more and lasts longer. Cotton is softer but does not handle wear or water as well.
Yes, many polyamide products can be recycled. Recycling cuts down on waste and helps the planet. Suzhou UNIKING New Material Co., Ltd. uses green ways to make eco-friendly polyamide.
Polyamide is found in car parts, electronics, sportswear, and medical tools. Its strength and heat resistance make it popular in many fields.
Think about how strong, flexible, or heat-resistant you need it to be. You can ask Suzhou UNIKING New Material Co., Ltd. for help and good polyamide choices.